QUAD
22 PRE-AMPLIFIER RE-ENGINEERING.
Last update 2018.
This page is about the Quad 22 preamp control units.....
During my 20 years as audio tech, aka "amp-worker", there was
interest in the "audio community" for
the early tubed Quad-II power amps and the Quad-22 control unit
aka integrated preamp. The original
Quad-22 has 2 x EF86 for MM phono amps and a pair of 12AX7 for
line level amps and the old fashioned
input - output terminals and general functions did not suit modern
expectations so I evolved a number of
ways of improving something made in 1950s to being much better
quality for the years after 1980.
If you are familiar with old Quad-22 preamps, my pictures and
schematics show what can be done.
Some owners wish to retain their pre-amplifiers exactly as they
were made in 1960 without modifications.
Where no modifications were wanted, but where something
malfunctioned, the original circuit only needs
a few R and C replaced, because the old carbon R tend to change
value or go open, and some C for RIAA
eq change quite a lot. It is possible to just replace all carbon R
with metal film and all C, and install a new
set of tubes and you have something that should last longer than
it has already, maybe 70 years.
I had one customer who had me repair his Quad 22 preamp and change
nothing because his record replay
system depended upon the Quad original circuit because of the many
available eq settings for many disk
recordings made before the RIAA eq curve was accepted by all
record makers. Quad made some of the
most reliable audio equipment, and one customer has been using his
Quad-II and 22 control unit since
1960 and he only needed to have it serviced 3 times. He has been
lucky. He has had me service his
Quad-22 only twice in the last 10 years.
But Quad-22 control amps like many others are not such wonderful
sounding amplifiers, and I believe old
Quad amps are not precious in their original state and can be be
much improved and simplified for better
sound and for compatibility with other modern amplifiers and
cabling. Quad-22 was designed for exclusive
use with Quad-II power amps which supplied the Quad-22 with power,
and the Quad-22 was designed to
be the only visible unit mounted in a timber console of an amp
system where the power amps were hidden
the console. The the power amps were turned on-off by switch at
Quad-22 control unit.
But many ppl did not care to build a console, they just bought
their Quad amps and an AM-FM tubed
tuner and it all just sat on a shelf or bench without with all
amps in view with the cabling, something that
drove some wives insane.
Many audiophiles are not married, so wife approval is not a
problem but they like all the gear in view,
and they like to mix and match with different power amps son the
preamp should be a stand-alone unit
with its own PSU and have modern gold plated RCA sockets only for
input-output.
Any electronic gear made after 1950 will have many parts which
have will have become faulty over the
many years. R and C values change, potentiometers can wear or
become noisy. There can be a serious
safety problem with original Quad mains wiring. But Quad-22 press
button switches are very reliable.
The only problem is that there are so many switch contacts in the
signal path at any given time. Sometimes
switch plastic buttons will disintegrate or fall off and get lost.
I have sometimes replaced all with metal
buttons which will never degrade. The potentiometers often wear
out and become noisy and need
replacement but just what with? the exact same types of pots are
hard to source.
Quad-22 do not need the complexity of the original switching
because only RIAA eq is needed, and radio
source inputs will be from AM-FM tuner with higher Vac input and
there's no need for tape input because
tapes and cassettes have gone extinct, and CD players or
multi-disc players are used or source is via DA
converter after a digital source which draws its signal from an
i-pod, PC sound card, lap top etc. Ppl want to
be able to select the normal modern range of line level inputs
sensitive to 200mV for aux for AM/FM tuner,
and 1.4Vrms from CD etc. Where they do play records, their
cartridge is MM making nominal Vo of more
than 3mV. It is possible to make a Quad-22 able to be used with an
MC cart but there is little room for it
and most ppl would use a phono MC step up transformer which can
increase the 0.3mA from MC to 3.0mV
and this works because most MC have output impedance < 20r, so
Rout of transformer < 2k0 which is fine to
suit 47k standard MM amp input resistance.
Fig 1. Reformed Quad-22 preamp, aka "22 Control unit" with
new back plate for RCA sockets.

The reformed Quad 22 preamp out of its case, in about 2001.
There are 7 twin triodes which replace the original two EF86 and
two 12AX7.
The gold plated RCA sockets make the unit compatible with most
cables with RCA plugs.
This sample was powered from a stand alone power supply.
Quad-II power amplifiers may still be used if :-
1. RCA input socket fitted.
2 each mono power amp has its own IEC mains input cable chassis
plug and its own mains switch.
The IEC sockets provide chassis earthing safer than original amps.
Modern users like to change amps
around often, so the preamp should have its own PSU and the
original Quad-22 case is far too small
to fit an PT and filter caps so the PSU must be in a separate
case, with 1.2metre 4-wire umbilical cable
with each wire rated for 5A and hard wired to preamp. End of cable
has octal plug to connect to
output octal socket on PSU.
The octal plug uses 4 pairs of pins, one pair for each cable wire,
and should have 1.5mm solid Cu
wire sweat soldered into each hollow pin, and have body of plug
filled with epoxy to make the plug
rugged.
The control knobs have a slightly different function to the
original and are set up from left to right as :-
Volume, Balance, Bass, Treble, HF Filter.
Of the original 5 plastic buttons, 3 were broken so I made new
aluminium buttons, hand engraved
them, and bolted them onto the metal switch tags M3 bolts+nuts and
with some Araldite.
The face plate of the amp itself was slightly altered since there
is no concentric balance lever on the
volume control and the 'QUAD' illuminated badge has been replaced
with an LED.
All the original ganged press button switches have been retained,
but with the simpler and more
effective circuit. 1/3 of the original contacts are used. I have
found these old switches to be more rugged
and reliable than the tiny switches mounted on printed circuit
boards found in much audio gear made after
1950 and which lasted less time Quad-22. Different R values for
volume (gain), and balance controls are
fitted.
The line stage gain amp and tone control amp is each fully
deletable, allowing a high Vac input to go
direct to volume control pot and only tube in signal path is ultra
neutral cathode follower before the
power amps. Long cables can be used between preamp and power amps.
The complex arrangement for multiple eq for 78 shellac records has
been abolished. There were
about 12 different contours for equalization of records produced
before 1955, but few people wish
to play them now, so the new preamp has only RIAA standard eq,
with hard wired passive RIAA filters
within the amp, rather than having the eq circuit for records in a
metal can that plugged into the back of
the original Quad. The plug-in cans tended to fall out and get
lost. The tape eq can has been entirely
deleted because nobody ever now uses the tape source used in the
early days of tape replay.
In the amp I modified, I have retained the LC filters to give a
steep 12dB/octave HF cut starting at
5 kHz or 7 kHz, or no cut at all. Having done that I found out how
useless such filters were for making
old records sound less noisy. Such filters remove the wanted
treble content and dull the music.
I have never used the filter feature. Bad noise from a 78 may
sound like a hailstorm on a tin roof, but
with a noise filter the noise just changes to a storm with big
drops of water. I know of nobody wanting
to play 78rpm records. Where a vinyl record is noisy, although it
looks clean, and without scratches,
most noise making junk is stuck in the grooves. The right way to
combat noise from vinyl is to clean
the record properly with a record cleaner machine and and with
solution of diluted polypropyl alcohol
with softens most junk that sticks in the record grooves. The
machine turns the record with a fine stiff
hair brush resting on record with suction air pump so the muck is
removed from grooves while the
record is still wet, and it is amazing how good old vinyl can be
without the mix of mould, 1965 chilli
con carne and cannabis ash etc, etc.
But anyway, I used the original well made Quad 22 filter
inductors, but I abolished the "variable filter
slope function" since it seemed to be a really utterly useless
function when I tried to use it with a
particularly noisy record in an original amp which worked OK.
The amp was repainted and aluminium knobs polished.
Fig 2. Reformed QUAD 22 preamp and a remote power supply,
2001.

The reformed preamp is on left, PSU on right. PSU was an old tubed
power supply I bought at a ham
sale for $2, but I completely rewired it to suit the needs of the
preamp, and I made the perforated steel
cover and painted it "gold" to match the preamp.
The power supply would normally be mounted well away from the
preamp on a shelf below the
control unit. A new umbilical cable was hard wired to the control
unit and octal plug fitted to suit the
octal power output socket on the rear of the supply.
Fig 3. Phone amp stage within reformed Quad-22 preamp,
2001.
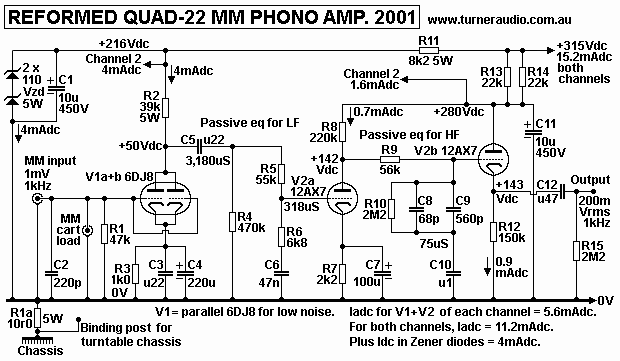
I have re-drawn the old hand drawn schematics using XP MSPaint.
The hand drawn schematics in
previous editions of this website were difficult to read. I hope
this shows those DIYers how to build a
fairly good phono preamp.
For each channel, phono input is to V1 6DJ8 grid, both halves in
parallel, feeding passive RIAA filter.
In theory, the parallel 6DJ8 should have at least 1/2 the noise
than 1/2 a 12AX7 because the gm of
parallel 6DJ8 is 8 times that of 1/2 of 12AX7.
The passive 3,180uS and 318uS time constant filters are between
V1a+b and V2a. The passive 75us
filter is betweenV2a and V2b and output is buffered by V2b which
is a cathode follower so Rout < 800r
and there are no unwanted HF losses.
The phono amp gives 46dB of gain at 1 kHz, which is plenty for all
MM cartridges, so that a typical
2.5mV or 1kHz at cart gives 0.5V output.
For MC a step up transformer will have to be used for low output
MC since I found the noise of the
6DJ8 was still too high for MC with outputs below 0.5mV. The
typical step up is +20dB, so 0.4mV
becomes 4.0mV at 1kHz. Most MC have Rout < 20r, so that
transformer output impedance = 2k0,
and the standard grid loading of 47k // 220p for MM does not load
the MC very much, and maybe 5k0
is wanted at RCA for MM cart load. Cartridge loading can be
changed from the default values shown by
using additional R+C mounted on an RCA plug and plugged into the
RCA socket shown beside R1.
Fig 4. Reformed Quad 22 control unit with tone control,
hi-cut filters, and output buffers, 2001.
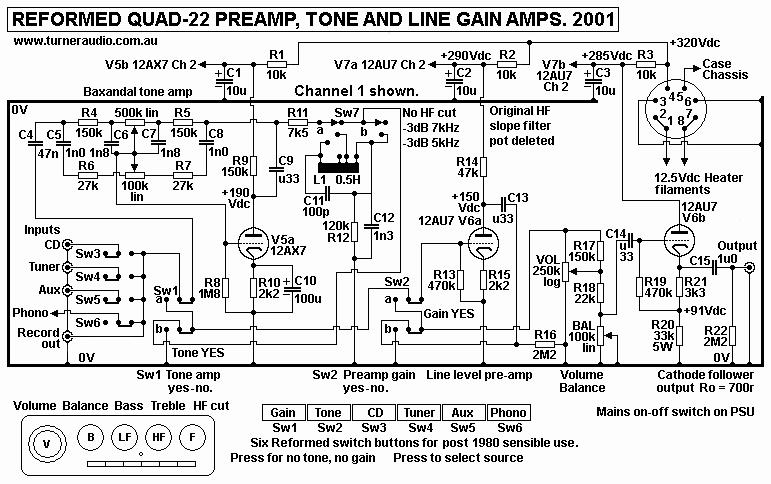
The reformed Quad-22 has different layout for the original 6 press
button switches and the 5 controls
with knobs. The lever for balance control and the variable HF
slope filter functions are gone.
The above schematic relates the schematic to the controls on front
panel is a much better way than
I showed with previous had drawn schematics.
Anyone could build the above schematic using modern parts. You do
not need to find a Quad-22
pre-amp But there used to always be one with every pair of Quad-II
power amps, and then not everyone
would like that. I found I was left with what ppl didn't want, but
also found ppl wanted preamps that
suited modern conditions so I used the good Quad-22 metalwork and
tube sockets to carry my
ideas forward.
The past is gone, and not all of it is worth preserving.
All the Quad press button switches are very good quality. They
should last 100 years at least,
with 64 years so far to 2018, and its better than anything made
after 1970. The metal is good, and
spring tension holding a contact against another is strong, the
sliding action of contacts and the right
kind of metal alloy keeps good contact for years, even if nobody
presses a button. The temperature
change inside the case is not huge with only 2 x EF86 and 2 x
12AX7, but enough to make all metal
contacts expand and contract enough to keep connections. In
squalid state amps made after 1970,
the contacts go open, spring tension lessens, contacts fatigue and
break, and planned obsolescence
makes some impressive audio gear become total junk. Quad got their
switches very right.
But the 5 pots used are prone to failure, track erosion, and I
suggest Alps Black, 27mm square
body types. In non Quad-22 based amps, I suggest rotary wafer
switches for input source selection
and gain and tone bypassing can work well and RS components carry
good stock which has 40mm
dia wafers with green plastic body.
The Passive L1 + C is used for sharp cut off -12dB/octave to
reduce bad record noise, but in fact is
a useless feature because where you remove noise above say 5kHz,
you also remove all audio, thus
making music dull.
I suggest there's enough good music to be listened to without any
reliance on what was recorded
before 1970.
Most classical music recorded in 1947 for LP has been better
recorded at some later time.
I knew a Lutheran minister who was 86 in 1997, and he'd played
Bach on 78 from a gramophone
mounted in back of a ute in 1940s, and to aborigines out west in
NSW, and they were quite utterly
gob-smacked. Some of those surviving records sounded OK is played
with RIAA eq. There were
12 different eq used for records before everyone agreed on RIAA.
Most early non RIAA sound OK
with RIAA eq on a preamp. A tone control can adjust things a bit.
Recording was once a very rough
process.
A later revamp of a Quad 22 in 2006 required whole set up to be
different; it will be dealt with further
down this page. But in this 2001 amp when tone and gain isn't
used, the input from the pole input from
the 4 input switches becomes directly connected to the top of the
volume control. If the following power
amp needs 1.0 to 2.0Vac for clipping, signal from a CD player does
not need to be amplified, and
usually there is no need for tone control or balance.
The tone amp has V5a = 1/2 12AX7 with Baxandal network within a
shunt NFB arrangement.
Such tone amps are sonically quite neutral and their presence in
signal path is impossible to discern.
The tone amp is unity gain, so for 1Vac input, you get maybe
0.95vac output, and output resistance
is nearly as low as a cathode follower, while input resistance is
high enough to suit the low Rout of
any source connected. I have rarely had any reason to use tone
control or balance control.
V6a 12AU7 line gain amp is a simple SET stage with local current
FB with R15 unbypassed which
would give. Gain = 13 approx with R15 bypassed with say 220uF. But
with R15 2k2 the gain is about 7.1,
and enough for anyone using an input source that was once the
standard 200mVrms max from an AM-FM
tuner etc. The gain of 7, increases Vout to same level as you
would have with CD player which makes
1.4Vrms max.
V6b 12AU7 has high input resistance with low shunt C because of
its cathode follower mode giving
Rout < 800r. This ensures low HF losses in 10metre long cables
with 1,000pF with -3dB pole at
200kHz!
Fig 5. PSU for reformed Quad-22 for 2001 and 2006.
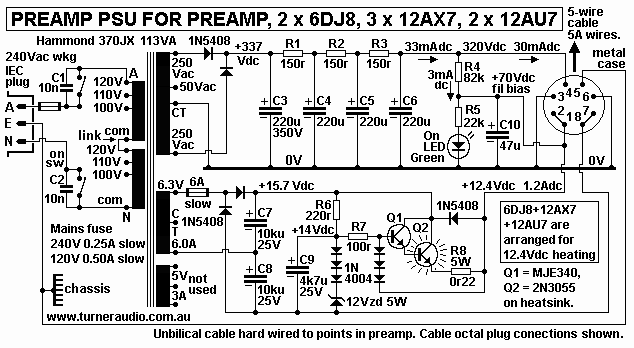
In this webpage edition, I have rationalised the PSU shown in Fig
5 to suit reformed Quad-22 for 2001 and
2006, and you should find it will suit very many tube preamps, not
just what I show here. Some adjustments
of R values in B+ CRCRC filter will be needed to keep B+ at the
wanted value, but in fact B+ could be
between +270Vdc and +350Vdc and the amps shown here will work OK.
I have chosen PT to be Hammond 370JX for 2001 amp with 7 x small
twin triodes which require 14.5W
for Idc heating.
Core has T32mm x S56mm and has optimistic 113VA rating.
The winding Rw is sufficiently low to allow its use here without
any worry of it getting too hot.
Primary can be for 240Vac, RwP = 6r2. HT sec is 250V-0-250V, RwHT
= 64r, is OK for 80W, but there is
less than 12W needed here.
Heater winding is 6.3V x 6A, Rw = 0.022r, for 37.8W max, but 17W
is needed here. The 5.0V sec will
not need to be used.
I thought of using Hammond 369JX but the transformer dimensions
are far too small at T25mm x S25mm
and winding resistances are very high and yet it has 50VA rating,
also very optimistic, but it may be OK for
2006 amp with only 4 x 12AU7. The 6.3V x 2.5A heater winding is
good for theoretical 15.8W, and
4 x 12AU7 need 8W, so it might be OK.
The best Hammond PT are their potted range which is a good idea
for any preamp to minimise stray magnetic
fields and to give low noise.
I suggest their 370DAXP rated for 76VA would be OK.
The primary can suit all international mains Vac including 240Vac
for Australia.
HT sec is 260V-0-260V which would give 350Vdc at the low 35mA
needed but it is easy to reduce this
with added R between each diode and first reservoir C3 above.
The heater is rated for 6.3V x 3.5A = 22W, so you should get
+15.5Vdc x 1.4Adc = 21.7W with some loss
in diodes. The tubes could use 12.4Vdc x 1.4A = 17.3W, and loss in
series regulator = 4.4W.
But 1.4Adc at 12.4V is only enough heater power for 4 x 6CG7 if
you insist on a better tube than 12AU7.
12AU7, 12AX7, 12AY7, 12AT7 need only 0.15A each 12.4 Vdc so the
1.4Adc could power 9 of them.
In my 10 tube
preamp I had to use a separate PT just for the heaters
because it is very uncommon for
many commercially made PT for tube gear to have more than a
minimum amount of heating power needed
for the output tubes intended for HT, and their input and driver
tubes, for example, 370DAXP could only
power 2 x 6L6GC plus say 2 x 12AU7 for a UL amp making 30W audio
Po, but heater power = 6.3V x 2.4A.
Always buy a PT with at least 50% higher VA rating that what you
KNOW you need.
In Australia, Jaycar and Altronics and Wes Components offer a
range of general purpose
30VA and 60VA PT for up to 30Vac with multi taps for 1A
or 2A.
For example, Jaycar cat no 6672 is 30VA for 240V : 30V x 1A with
CT at 15V and 4 other taps, and it
could be used for full wave rectifier to make +19Vdc x 1.5Adc.
Jaycar 2165 is 60VA for 249V : 30V at 2A with CT, or 24V with CT,
or 18V with CT.
Sadly, these companies don't supply any transformers for 240V
primary and a range of higher Vac to make
up to +350Vdc.
But you could have Jaycar 2165 60VA PT for 240V : 30V, and
have a Jaycar 6672 30VA for 240V : 30V,
and use the first for Idc for heaters, and connect the other so
its 30V sec becomes a primary and you get
240Vac which would easily give +320Vadc at 35mA using a bridge
rectifier. These two PT should cost no
more than AUD $60.00.
The heater Vdc supply derived from 60VA tranny is biased at +74Vdc
which means all triodes with
cathodes at Ek under +10Vdc have cathode to heater Vdc = about
60Vdc, but within the 90Vdc max
rating.
Where some triodes operate as cathode followers, their cathodes
may be at +150Vdc so the cathode to
heater Vdc = about 80Vdc, but within rating. But of course in
numerous guitar amps the cathode followers
used to drive "tone stack" networks often have heaters at 0V and
cathode at +200Vdc, and seldom did I
ever have to remove a triode, usually 12AX7, for arcing or short
circuit between cathode and heater.
I have seen a few tubes develop lowish resistance between cathode
and heater and where heating is
done with Vac, there can be 50Hz hum entering signal path. Only 2
cases in hundreds of repair cases
where tubes were old worn out, over 18 years of service work, and
where there Vdc difference was less
than 10Vdc.
Fig 5A. Preamp PSU with two x 240V : 30V mains PT.
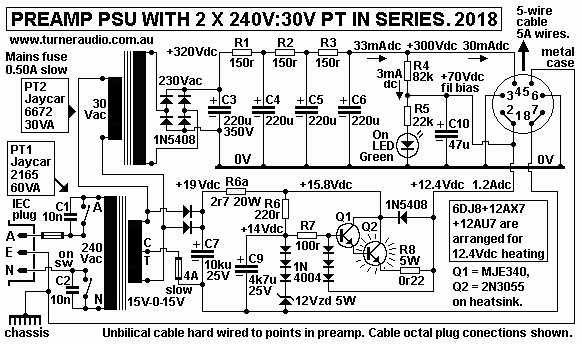
Fig 5A shows PT1 60VA for 240V : 30V x 2A max and PT2 30VA PT for
240V : 30V x 1A max.
The max heater power from PT1 = +22Vdc x 1.2Adc = 26.4W.
The max B+ power from PT2 = +320V x 33mAdc = 11W.
The power into PT2 30V primary = 12W, so PT1 has to provide 26W +
12W = 38W.
PT1 is rated for 60VA so it should not overheat.
These two PT are open frame types with considerable magnetic
leakage so I suggest they be
mounted inside a mild steel sheet box and cores oriented 90degrees
to prevent magnetic field
of one interacting with the other. They could be potted, but
because PSU is on a remote chassis
to amp with 1.2Metre cable at least, the potting is not needed but
the box must have plenty of
ventilation holes to prevent the hot-box syndrome.
In Fig 5 and Fig 5A, the Vdc circuits are identical but the 5A use
of 2 PT will probably give lower
B+ because of the probable Vac losses with series PT.
if you do not want a lower B+ you are free to use a filter choke
and make it CLC with
470uF + 8H + 470uF using Hammond 193D choke with Rw = 75r and
weight = 1.5kg, and
about same size as PT1. Vdc drop across 75r = 2.5Vdc, and the V
ripple at second C = 0.1mV,
and probably low enough.
Fig 5 +5A show series element regulator to give 12.4Vdc heater
supply using Q1 MJE340 and
Q2 2N3055 which needs a heatsink which could be the rear panel of
the PSU case.
This assumes PT1 and PT2 are inside their own case which is inside
the main case with the
PSU circuits including the regulator, so real panel of main case
can be 3mm Aluminium.
The bjts are Darlington connected to much increase Hfe, and reduce
base input current. The
ripple at top of C7 with 1.2Adc is 0.53Vrms. The Vac at Q1 base
can be substantial because
12Vzd +1N4004 have high enough impedance so that there is
considerable Vac at base.
Therefore I suggest you try C9 4,700uF bypass cap. This should
reduce 100Hz Vac at Q2
emitter output to < 1mV.
During normal operation for 2001 amp, Vce for Q2 can be 3.0Vdc and
if Idc = 1.2A, the heat is
3.6W, enough to create some heat inside the case, so lots of holes
need to allow air flow and
to allow heat to get out of case. But rear panel area = 22cm x
10cm = 440sq.cm, both sides,
so T rise will be low of heat power < 5W.
You always must think about heat with tube gear.
In the 2006 PSU for preamp there were only 4 x 12AU7 for about 8W
of heating power with
12.5Vdc x 0.6A so heat in regulator = 1.8W which was easy to deal
with, and case did not get hot.
A preamp PSU case needs plenty of ventilation holes or else
contents will overheat, causing
increased metal oxidation, and maybe cause capacitors to fail.
In Fig 5, if heater Idc increases to 3.0Adc, Iac in 6.3Vac winding
will increase to over 6A and
6A fuse will blow.
In Fig 5A. if heater Idc increases to 3.0Adc, Iac in each 15V
winding will increase and maybe
blow 4A fuse.
Fuse values MUST be chosen to cause fuse to blow if Idc doubles
for more than 20 seconds.
There is high initial Idc at turn on when all heaters are cold and
have 1/2 their hot resistance.
Getting it right takes time.
There other possible refinements with LM317K 3Adc regulator in TO3
package and with slow
ramping up of Vdc.
In 2006 reformed Quad-22 with 4 x 12AU7, I wound the power
transformer myself with
B = 0.85Tesla and with T32mm x S32mm using GOSS from about 1980.
It ran cool,
and didn't make any noise or vibrate. I have lost the full
details.
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Fig 6. A later reformed Quad-22, front panel, 2006.
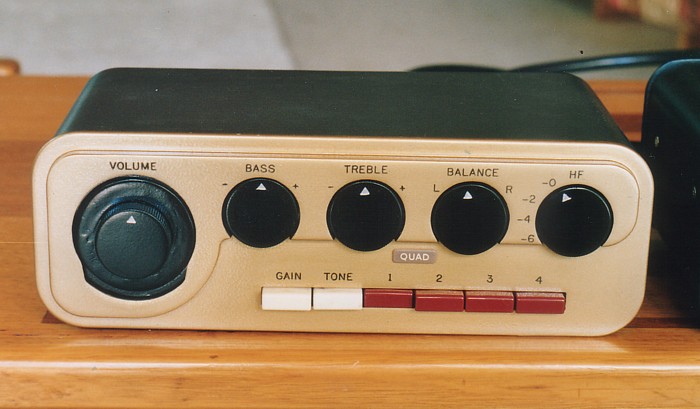

Source selections are by pressing interactive switches 1,2,3,or 4.
For excluding the gain amp, press the gain switch, and to exclude
tone control, press tone control,
and for both, press both in at once so they stay in; these are
interactive switches, but are easy to
get used to.
Fig 7. 2006 schematic of what is in the Fig 5 Quad-22
above......
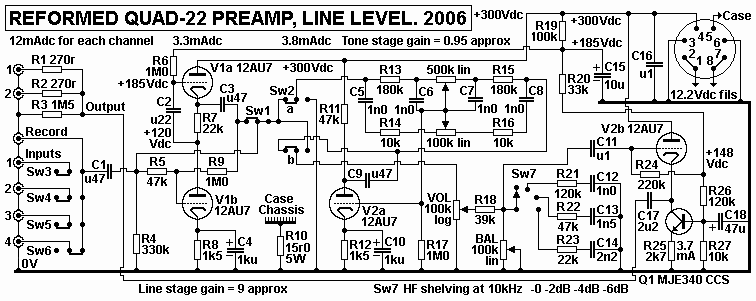
Fig 7 is another reformed Quad 22, there is no phono stage, and if
you want one, build the above
Fig 3 phono amp.
But my customer did not want a tubed phono and already had
something he thought was better than
anything else. Fig 7 has V1a + V1b set up as a Bootstrapped
Follower which became my favourite
form of SE signal stage because it has about -20dB less THD than
the normal use of Idc to anode
via a resistor, as used for V2a.
The BS follower has Rout nearly as low as a pure cathode follower
and in this case its open loop gain
about 16. R5 + R9 form local shunt NFB network to reduce gain to
about 9, and probable THD at
typical 1Vrms output might be less than 0.03%, mainly 2H, and it
sounds just fine.
With Sw1 pressed in, The input after C1 is taken directly Sw2a and
tone control R+C network.
V1a still works, but its output does not go anywhere.
The R+C tone network is a Baxandal local shunt NFB network which
became very common in the
best hi-fi amps because it had low noise, used linear pots which
are far more likely to be matched for
each channel and the NFB means that open loop gain of V2a of say
14 is reduced to about 0.9 so
THD is also reduced and nobody has ever been able to tell me if
the tone control stage is in the signal
path or not. You can press tone switch to exclude the tone
control, and hear absolutely no change to
audio quality. The tone control in many amps gave +/- 20dB max
boost or cut at 100Hz and 10kHz,
but in this amp there is about +/- 9dB maximum boost and cut to LF
and HF, which is plenty.
V2a is a SET gain triode with R11 47k to +300Vdc. Its THD is not
as low as V1a+b but the local
shunt NFB of tone R+C network reduces THD by factor of 0.06, so if
TH without NFB was 0.1%
with no NFB, THD with NFB is < 0.01%, and you cannot complain
about that.
The "unity gain" stage such as tone control amp has more THD when
bass or treble is boosted, but
usually there is little need to ever use it because these days
most recording cannot be improved by
boosting or cutting HF of LF above and below 1kHz.
However, I had customers who complained that CDs were harsh
sounding, and they wanted to
adjust treble down a bit, and I figured out that a shelving
network gave them what they wanted with
the switchable R+C networks which work from rotary switch Sw7.
This switch was once used to
have sharp cut off for HF but that didn't please too many ppl.
What my switched shelving networks
do is give flat response to say 1kHz, then the response falls at
less than -6dB / octave and flattens
out to a shelf that is -2 to -6dB at 10kHz. This reduces all the
HF above say 2kHz by about the same
amount. Some speakers have been made which have too much treble
because the makers don't pay
any attention to making them with a flat response. Makers
frequently make speaker with a loudness
contour, bass and treble can be 6dB louder than 1kHz, all because
dopey buyers in shops will decide
on what "has the most detail". I found I had to re-engineer very
many speakers with atrocious F
responses. But some hi-end speakers have too much treble, and the
listening room can give
problems, so hence the shelving networks.
V2b is a cathode follower output stage with CCS cathode current
sink using MJE340. Thus the only
R load for output is the input resistance of a power amp, usually
above 47k. THD at 1Vrms < 0.04%.
Note that this particular Quad-22 didn't have enough switches on
S1 to have more than one switch used
for gain deletion so when the gain stage is switched out the input
source is still connected to the R5 47k
input feed to V1a.
Thus input resistance at 1 to 4 inputs is about 50k, and most
music source components such as CD
player have output resistance of 600r or less. Even if a Vac
source has has Rout 10k0, the input
resistance of the amp will not cause any problems.
V1b and V2b have fixed bias applied from R divider
R19+R20+R27+R27. The divider provides
about 11.4Vdc to base of MJE340 CCS, well bypassed by C18 47uF and
Vdc is kept constant across
R 25 2k7 hence collector resistance is well over 1 megohm.
Fig 8. Reformed Quad22, 2006, rear panels of hand made PSU and
rear panel preamp with 4 x 12AU7.

The umbilical cable is nicely flexible and will curl up easily.
Before April 2018, I did not give much information on the power
supplies.
Fig 8 shows the rear panel of the PSU I made with same box
dimensions as the original Quad-22.
There is IEC for mains input, and two octal sockets for B+ =
+300Vdc, 12.4Vdc for all heater
filaments biased at + 74Vdc, and to link Earth for cases and
chassis, and for a 0V bus rail
which is NOT directly connected Earth at any point. This usually
keeps hum noise to extremely
low levels.
Fig 9. Reformed Quad-22, 2006, with cover off.
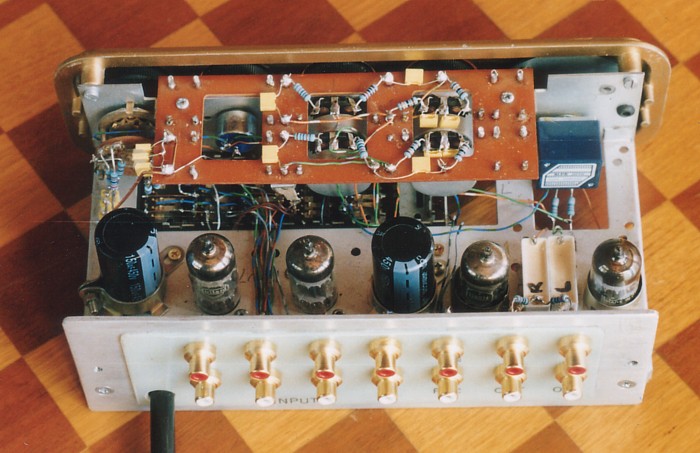
The 4 x 12AU7 can be seen standing in the original McMurdo tube
sockets. There are
two 150uF caps mounted above chassis in the line of tubes, because
the PSU did not
contain all B+ rail caps in its box. Experience since 2006 taught
me there is no need
for B+ rail caps in the amp case, other than 0.1uF from +300V to
0V rail.
The Alps Black volume pot can be seen on right side.
The existing Quad board for components for the tone controls was
retained but fitted with
new yellow polyester capacitors and new light blue 3/4W Welwyn
metal film resistors.
Two 4 mm screws hold the cover onto the amp chassis.
Fig 10. Reformed Quad-22, 2006, under chassis wiring.
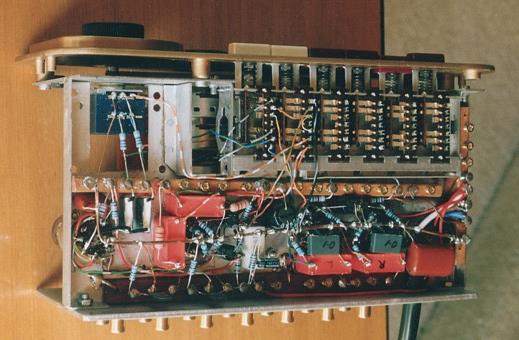
It is very crammed inside this amplifier!
You can see that 4 rows of switches are not used because there is
a second side to the switch
bank hidden under what is seen.
All the original turret connectors used in Quad-22 were removed
and replaced with fibre strips with
brass plated screws to give a better range of connection points.
All the coupling capacitors are red Wima polypropylene MKP,
0.47uF, 630V rated, except output
caps from V2b cathode which are white polyester 2u2.
The thick solid wire west to east under tube sockets is the 0V bus
rail and allows 3 dimensional
wiring with very short leads, separate from the case and chassis.
Wiring for B+ rail voltages and heater wires is with well
insulated stranded wiring but wires carrying
signal is 0.6mm solid hook up wire taken from a multi pair
telephone cable which had about 50 wires
of different colour coded wire. This makes it easy to trace wires
in service work. And it sounds well.
To re-engineered amps
To Index Page 









